CHIA Publishes New Report on Hospital Readmissions in Massachusetts
DATE: December 18, 2018
CHIA today released its most recent analysis of unplanned hospital readmissions in Massachusetts in Hospital-Wide Adult All-Payer Readmissions in Massachusetts: SFY 2011-2017.
Key findings from the report:
-
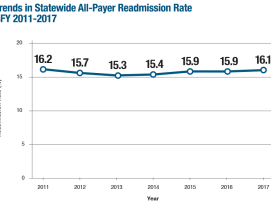
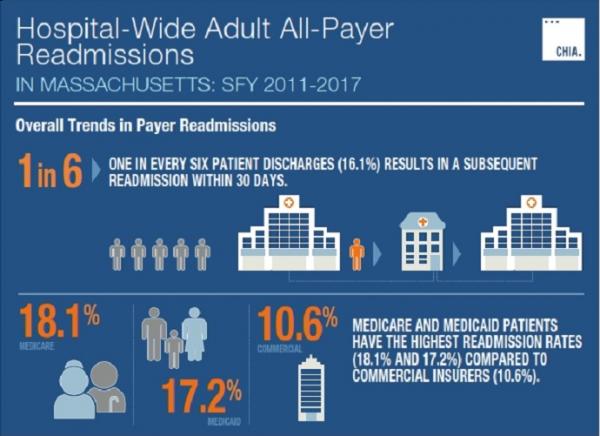
- The unplanned, all-payer readmission rate for Massachusetts acute care hospitals has increased since 2013, rising to 16.1% in 2017.
-
- Medicare and Medicaid beneficiaries had the highest rates of readmission (18.1% and 17.2%, respectively) and accounted for 84% of all readmissions.
-
- Readmission rates also varied by geography, from a low of 13.8% in Cape Cod to a high of 20.2% in Fall River.
-
- From 2011 to 2017, readmission rates increased for adults aged 18-64 and decreased for adults aged 65 and over.
-
- Heart failure, sepsis, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) were the top three discharge diagnoses leading to the most readmissions in 2017.
- A small percentage (7%) of hospitalized patients accounted for over half (59%) of all readmissions.
This report is also accompanied by a databook, technical appendix, and, for the first time, an infographic
 .
.
